Key Takeaways:
- The EU Resilience Act enhances digital product security and resilience against cyber threats. It sets mandatory security standards for all digital products, including software and IoT devices. (European Union, Policy and legislation | Publication
- Manufacturers and suppliers must comply with CRA standards, improving overall security. The Act balances risks and benefits, reflecting user interests and promoting broad stakeholder involvement.
- Despite implementation complexity and stakeholder conflicts, the Cyber Resilience Act emphasizes democratic participation and considers community feedback.
What is the EU Cyber Resiliance Act (CRA) 2024?
The EU Cyber Resiliance Act (CRA) is a regulation established by the European Union to enhance the security of digital products and ensure resilience against cyber threats. Recognizing the inadequate level of security in millions of electronic products, the EU Cyber Resiliance Act (CRA) aims to protect these devices across Europe.
Featured Source:
What is Cybersecurity? | Types and Threats Defined
The EU Cybersecurity Resilience Act’s primary goal is to establish security standards for all digital products and services, including software and IoT systems. This proposal requires manufacturers and suppliers to adhere to these security levels, thereby enhancing the digital ecosystem's overall security and providing users with stronger protection.
Positive Effects:
- Risk Reactions: The Act addresses security risks, creating a safer environment.
- Reflecting People's Interests and Preferences: It ensures that users' demands for security are better addressed.
- Shifting Control from Big Tech to a Wider Audience: It allows more stakeholders to participate in the decision-making processes.
- Fair Distribution of Benefits and Burdens: It ensures that everyone benefits equally from digital security.
Challenges:
- Complexity of Implementation: Setting and enforcing security standards can be time-consuming and costly.
- Conflicts of Interest: Different stakeholders may have varying security needs and priorities
The proposed law underscores the importance of democratic participation and ensures that community views are considered when setting security standards. For example, OpenAI has made efforts to integrate community suggestions, secure funding, and promote a democratic process for individuals submitting proposals for AI projects.This involves directly incorporating feedback and suggestions from various communities.
Featured Source:
Democratizing AI: Multiple Meanings, Goals, and Methods
What does the Cyber Resiliance Act do?
The European Parliament defines this law as follows: "The Cyber Resilience Act aims to strengthen the cybersecurity of digital products and ancillary services, making the EU more resilient to cyber threats by ensuring that products with digital elements are designed, developed, and maintained in accordance with state-of-the-art cybersecurity practices.
This legislation imposes specific requirements on manufacturers, developers, and distributors to address vulnerabilities and provide timely updates, thereby enhancing the overall security and trustworthiness of the digital environment."
This definition clearly outlines the purpose of the law and how it is to be implemented.The Act ensures that digital products are designed, developed, and maintained according to the latest cybersecurity practices. It imposes specific requirements on manufacturers, developers, and distributors to address vulnerabilities and provide timely updates. This, in turn, improves the overall security and trustworthiness of the digital environment.
Why do we need CRA? I Evidentiary examples
We can understand the necessity of this law from past cybersecurity incidents that have caused significant public concern. Looking back, there have been many cybersecurity breaches, and this situation has become even more critically important with the development of AI. Below, I would like to remind you of three examples of such incidents:
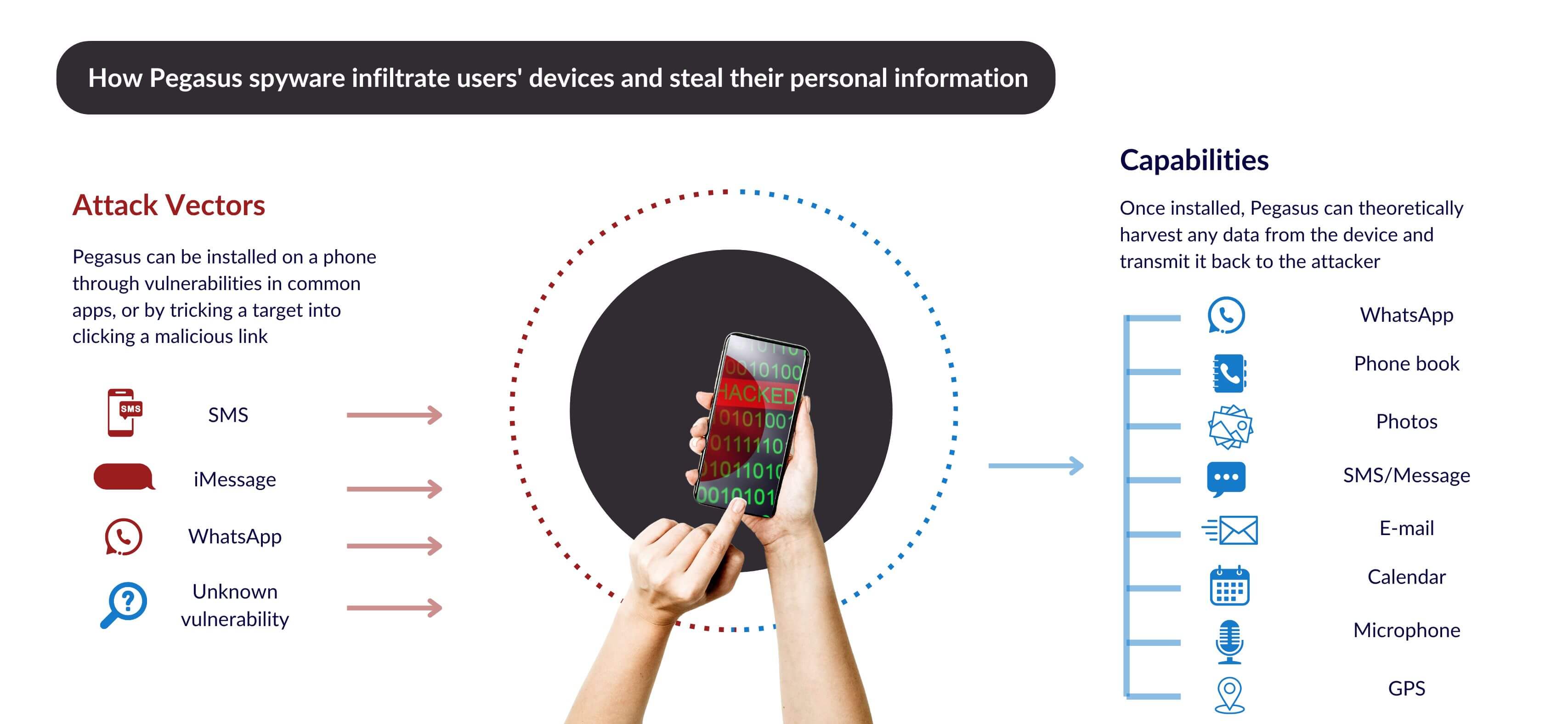
1. Pegasus Spyware
Pegasus spyware was a software that exploited security vulnerabilities in mobile phones to infiltrate users' devices and steal their personal information. Developed by the Israeli NSO Group, this software provided access to the camera, microphone and messaging applications of the target devices.
Details:
- Pegasus caused a major stir by infiltrating the phones of many journalists, activists, and politicians.
- The software could infect target devices through zero-click attacks, meaning that the device could be infected even if the user did not click on any link.
- Since Pegasus was difficult to detect, it can operate for a long time without being noticed.
Such spyware clearly demonstrated how dangerous security vulnerabilities can be by threatening individuals' privacy and security. I find this situation important as it reminds us of the need to make digital products more secure and to protect users.
2. WannaCry Ransomware Attack
WannaCry was a ransomware attack in 2017 that affected computers in approximately 150 countries worldwide. This attack occurred by exploiting a security vulnerability in Windows operating systems.
Details:
- WannaCry encrypted users' files, making them inaccessible, and threatened to delete the files if the ransom was not paid.
- This attack affected a large number of institutions, including hospitals, banks, and many large companies, causing operational disruptions.
- Although security patches were quickly released to prevent the spread of the attack, the damage was significant and many institutions experienced serious financial losses.
The WannaCry attack demonstrated how quickly cybersecurity vulnerabilities can spread and how wide-reaching their impact can be.
3. Cyber Attacks on Oil Facilities in Europe
Imagine it’s 2022, and oil facilities across Europe are suddenly thrown into chaos because of cyberattacks. It’s like a scene from a thriller, but it’s happening in real life.
Details:
- These attacks managed to slip into the critical systems of oil distribution terminals in places like Germany, Belgium, and the Netherlands.
- The attacks led to disruptions in oil supply and serious interruptions in the supply chain.
- The authorities who looked into it said these attacks weren’t just random acts of mischief. They were complex and carefully orchestrated, leading many to believe that either an organized crime group or a state-sponsored actor was behind them.
The energy sector, in particular, felt the shockwaves. This sector isn’t just about keeping the lights on; it’s the backbone of our daily lives and economies. When it gets hit, everything feels the tremor. That’s why we need robust laws like the Cyber Resilience Act to step up our defenses.
These laws aren’t just about keeping hackers out; they’re about safeguarding our lives and ensuring that when you flip a switch, the lights still come on. It’s about making sure our digital and physical worlds are secure against these kinds of shocks, protecting everyone from individuals to entire governments.
European Parliament approved the Cyber Resilience Act (“CRA”)
The European Parliament approved the Cyber Resilience Act (CRA), a comprehensive regulation aimed at enhancing cybersecurity for digital products and services, on March 12, 2024.
You can access the approved text here.
This legislation aims to counter the growing threats from cyberattacks and ensure that digital products are designed, developed, and maintained with robust cybersecurity measures. The CRA introduces specific requirements for manufacturers, developers, and distributors to protect against vulnerabilities and aims to increase the overall reliability of the digital ecosystem.
The Cyber Resilience Act will strengthen the cybersecurity of connected products, address security vulnerabilities in hardware and software, and make the EU a safer and more resilient continent. Parliament has protected supply chains by ensuring that critical products such as routers and antivirus software are a cybersecurity priority.
We have supported micro and small businesses, ensured better stakeholder engagement, and addressed the concerns of the open-source community while remaining ambitious. We can only overcome the cybersecurity emergency ahead of us in the coming years by working together successfully.
European Parliament member Nicola Danti (Renew Europe, IT)
Key Points About the CRA for Everyone
1- Keeping Your Devices Safe:
Think of the CRA like a set of rules to keep all your gadgets like smartphones and tablets safe. Just like you need to keep updating your favorite game to get new levels and fix bugs, these rules make sure your digital devices get regular updates to stay secure.
2- What Makers and Developers Need to Do:
Imagine if you were designing a new toy. You’d want to make sure it’s safe before other kids play with it, right? The same goes for the people who make your apps and devices. They need to check for any problems and fix them fast, letting users know about it too.
3- Applies to Lots of Things:
The CRA isn’t just for one type of gadget. It covers a wide range, from your smartwatch to the software that helps you do homework.It’s like a big safety net for all your digital stuff.
4- Watching Out for Risks:
Companies need to keep an eye out for any security issues, kind of like how a lifeguard watches over swimmers. If they spot a big problem, they have to tell the right people quickly to keep everyone safe.
5- Helping You Make Safe Choices:
When you buy a new phone or laptop, you get info about how safe it is. This helps you pick the best one, just like you’d choose the safest bike helmet.
6- Serious Consequences for Rule-Breakers:
If companies don’t follow these rules, they can get into trouble, like getting a big fine. This makes them take security seriously, so you can trust your devices are safe.
7- Working Together Around the World:
The CRA encourages countries to team up to fight against bad actors in the cyber world. It’s like a global neighborhood watch for the internet, making sure everyone is looking out for each other.
The Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) is a big step to improve cybersecurity in the European Union. It sets high standards for digital products and services to protect people and businesses from cyberattacks. This act aims to make the digital world safer for everyone. All companies need to follow these rules and take responsibility.
In the future, every company will need to change their plans to meet these new rules. This process might seem complicated. Setting up and keeping security standards can take a lot of time and money.
If you’re wondering where to start, the answer is simple: download and read the Cyber Resilience Act Requirements Standards Mapping document from ENISA. This will help you know what your company needs to do and plan for the changes.
Additionally, I will have some recommendations on this topic in the following sections of the text.
Importance of Cybersecurity
In light of the details provided above, it is clear that cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important in the digital age. The latest Eurobarometer surveys conducted by the European Commission in May 2024 also confirm this reality. These surveys demonstrate that the vast majority of citizens are concerned about digital threats and prove that stronger cybersecurity measures are necessary.
Eurobarometer Findings:
- 71% of survey participants believe that cybersecurity is a high priority among companies.
- 44% of companies with open positions in the field of cybersecurity report facing challenges due to a lack of candidates.
- The study reveals that 76% of employees in cybersecurity-related roles do not have any formal qualifications or certified training.
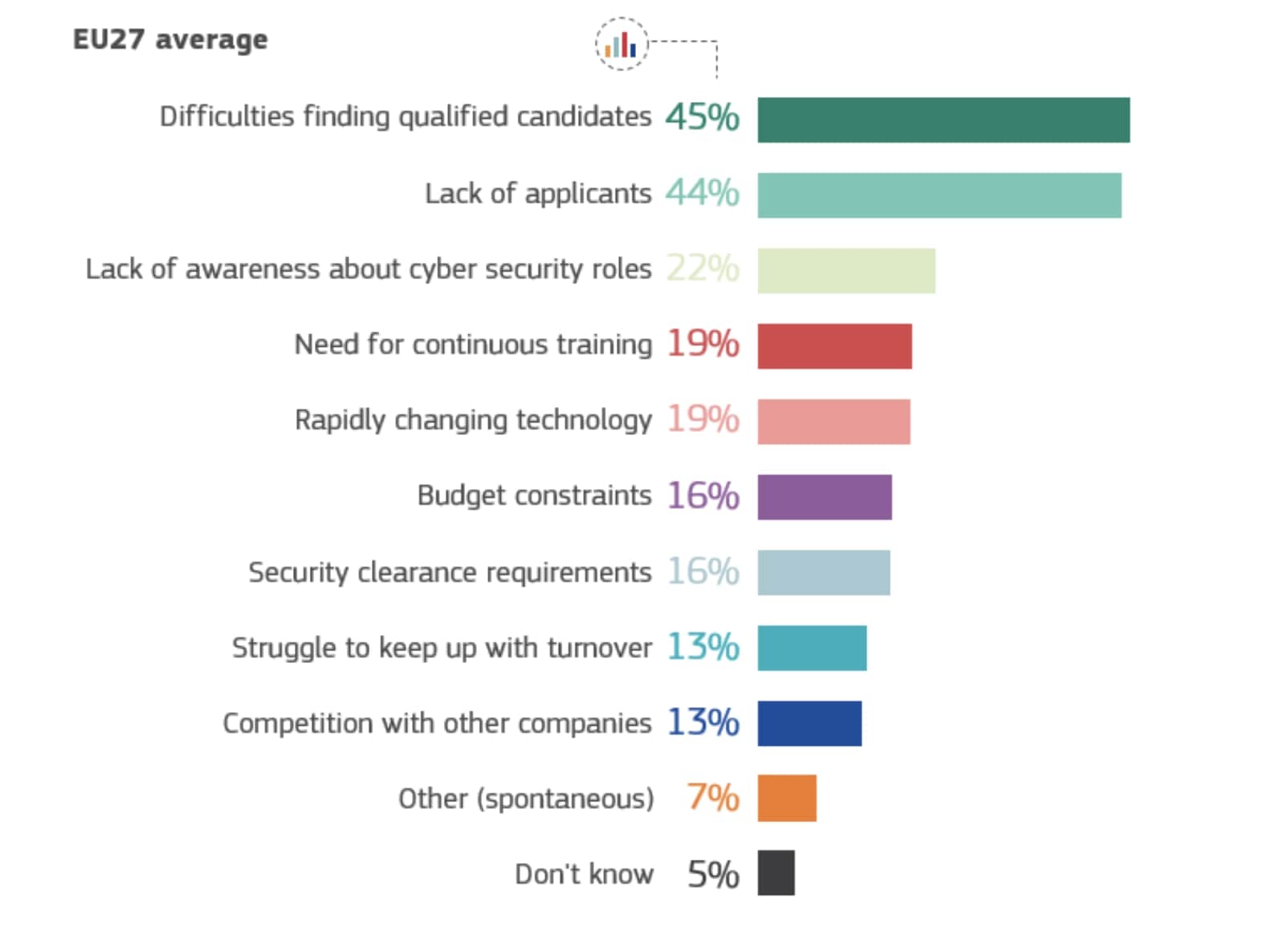
These data prove how important it is to enhance cybersecurity measures and develop digital skills. We can all foresee that without a strong cybersecurity infrastructure, individuals and businesses will face significant risks. We need to make the necessary guidelines, receive appropriate training, and implement crucial security measures like the CRA.
EC-Council Training
Training and skill development are of critical importance to deal with cybersecurity threats. In this regard, the EC-Council offers globally recognized cybersecurity certifications and training programs. These programs provide various training options that individuals and organizations should undertake to be better prepared against cyber threats.
Highlighted EC-Council Trainings:
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): This training focuses on ethical hacking skills. It teaches you how to find and fix system vulnerabilities in a secure and legal manner.
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM): This certification helps you develop leadership skills in managing information security within an organization.
- Certified Chief Information Security Officer (CCISO): This program equips you with the skills needed for high-level information security management, aimed at executive positions.
These training programs are essential for building cybersecurity skills and ensuring digital security. The European Commission's research highlights the importance of investing in cybersecurity education. EC-Council's programs will help create a safer digital environment by making both individuals and organizations more resilient to cyber threats.
Conclusion
You want your gadgets and apps to be safe and secure, right? The CRA is here to make sure they are. Whether it’s protecting your personal data or keeping your devices free from hackers, these rules are designed to keep you safe.





