Key takeaways
- Cybersecurity is the collection of technologies, processes, and practices designed to protect our devices, computer systems, networks, and stored data. Today, ensuring the security of devices that can connect to the internet from anywhere and the increasing online interactions is crucial for protecting personal and corporate data.
- Cybersecurity identifies suspicious activities, provides protection against malware, and secures data through encryption. It protects our digital assets from unauthorized access, theft, damage, and cyber attacks. This involves a range of measures such as authentication, access control, and threat detection.
- There are six main types of cybersecurity: Information Security, application security, network security, cloud security, IoT security, and critical infrastructure security.These types protect a wide range of technological infrastructures, from power plants to smart devices.
- As the importance of data privacy and cloud security grows, cybersecurity teams will continually need to reskill and adapt. In the coming years, ongoing threat management and the development of authentication systems will be central to cybersecurity strategies.
Introduction to Cyber Security and Data Protection
In a world where every device is connected, there are many conveniences this offers us. For example, being able to work easily from anywhere using a smart phone, laptop, or tablet with an internet connection sounds great. Easily planning your social activities or business meetings, managing your calendar, shopping with a click, or making a doctor's appointment are just a few of the activities that make our lives easier today thanks to the internet.
In addition to these conveniences and life-enhancing options, there's an important reality to remember: The internet doesn't always provide a secure space. The ease of connected data also means that threats from bad actors can cause significant damage. Cyber attacks are increasing daily and pose a major threat.
At this point, cybersecurity initiatives come into play to protect our data and, consequently, our lifestyle. Consumers are more careful about where their personal data goes, governments are enacting regulations in many areas from health systems to population control, and companies are investing more in protecting their operations against cyber attacks.
So, what is cybersecurity and why is it so crucial?
Simply Explained: What is cybersecurity?
On the whole, cybersecurity is the practice of protecting the devices we often use, including smartphones, laptops, and tablets, the corresponding computer systems and networks, as well as the data contained therein. Indeed, the essence of cybersecurity lies in ensuring the privacy, lack of distortion, and accessibility of one's own technological resources. Stated differently, cybersecurity meaning refers to the methods, technology, and processes, covering online and in-the-workplace servicings, which protect them against cyber attacks and any other type of unauthorized access.
In fact, the primary goal of cybersecurity is to protect all the corporate and personal assets from external and internal threats and malicious attacks and thus contribute to cybersafety raising and cybersecurity solutions development.
The prevention of damage to, protection of, and restoration of computers, electronic communications systems, electronic communications services, wire communication, and electronic communication, including information contained therein, to ensure its availability, integrity, authentications, confidentiality, and nonrepudiation.
- NIST Cybersecurity Definition
Why is it important?
Cybersecurity is crucial because smartphones, computers, and the internet are now essentials of modern life. We share personal information in every area from online banking and shopping to emails and social media. Therefore, taking steps to prevent cybercriminals from accessing our accounts, data, and devices is more important than ever.
On an individual level, a cybersecurity attack could result in everything from identity theft to extortion attempts, from fraud to the loss of important data like family photos.
Looking at it from a corporate perspective, personal data is present in banks, hospitals, and all other government institutions. Securing this data and the organizations themselves is vital to maintain the safe functioning of society. With the rise of AI technology, the risks are increasing, making cybersecurity a topic we discuss more and focus on more intensely.
What does cybersecurity cover?
Cybersecurity involves protecting a broad range of digital assets, from sensitive data and computer systems to networks and everyday devices. This cybersecurity definition emphasizes that the core aim of cybersecurity is to safeguard these assets from unauthorized access, theft, damage, and various cyber attacks, reflecting its fundamental cybersecurity meaning.
Cybersecurity solutions include advanced threat detection systems that help identify and mitigate threats by spotting suspicious activities and potential security weaknesses. These systems continuously monitor network traffic to detect and analyze deviations that could signal an attack.
Moreover, cybersecurity uses encryption, secure authentication, and access control to protect personal information, thus enhancing cybersecurity awareness. It also defends against malicious software with antivirus programs, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
Cybersecurity also plays crucial roles in mitigating DDoS attacks, training employees on potential threats, and ensuring legal compliance, highlighting the cybersecurity roadmap for maintaining security. Incident response and recovery procedures are critical for minimizing damage post-attack damage, illustrating reason cybersecurity is vital for any organization.
What are the main types of cyber security?
1- Information Security
Information Security means protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of data for organizations or individuals. This field involves safeguarding information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, alteration, or destruction.
In today’s world, where data breaches and cyber attacks are increasingly common, information security is a strategy that must be implemented to reduce the risks faced by both organizations and individuals. A well-planned information security strategy allows organizations and individuals to operate securely by protecting valuable information.
Measures that can be taken:
- Comprehensive Security Policies and Procedures: Organizations should develop and implement comprehensive policies and procedures to ensure information security. These policies are crucial for determining who can access information and how and where it will be stored.
- Training and Awareness Programs: Educating employees about information security and teaching them about security threats, risks, and proper security practices can reduce human errors and prevent security breaches.
- Security Software and Hardware: Using security software and hardware such as antivirus programs, firewalls, and encryption technologies helps protect information, creating a defense line against malicious attacks and ensuring data security.
- Regular Risk Assessment and Security Audits: Organizations should regularly perform risk assessments and conduct security audits. These processes help identify potential vulnerabilities and facilitate proactive measures to maintain security.
2- Application Security
The rise in digital transformation and online service usage has made software applications more vulnerable to malicious attacks.Application security is critically important, especially in sectors handling sensitive data like finance and health services.
Measures that can be taken:
- Secure coding practices and continuous security testing.
- Advanced static and dynamic code analyses.
- Continuous security through software updates and patch management.
3- Network Security
Network security controls access to corporate data and systems by preventing malicious attempts. The rise in cyber attacks during the pandemic has made network security even more crucial. With the increase in remote work, corporate networks have become more vulnerable to attacks. Network security is now more important for companies to prevent data leaks and ensure business continuity.
Measures that can be taken:
- Strong user authentication processes.
- Effective antivirus programs and intrusion detection systems.
- Continuous network monitoring and proactive threat management.
4- Cloud Security
Cloud security is crucial as the use of cloud-based systems increases,particularly to protect sensitive information stored in these systems from unauthorized access. While cloud technologies offer flexibility and accessibility, these features can also lead to security vulnerabilities.
Cloud computing has been adopted by many businesses due to its flexibility and cost efficiency. However, the high density of data on cloud platforms makes these systems susceptible to security breaches. A secure cloud service is essential for businesses to maintain data security and customer trust.
Measures that can be taken:
- Encryption techniques and multi-factor authentication.
- Access control mechanisms and continuous security audits.
- Threat analysis and proactive security strategies.
5- Internet of Things (IoT) Security
The rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Augmented Reality (AR), and the Internet of Things (IoT) technologies is transforming how we conduct our business processes and simplifying our work. These technologies enhance our efficiency by handling routine tasks, allowing us more time for tasks that require human insight and creativity.
Featured resource:
AI Workforce Revolution: The Augmented Future
IoT devices are increasingly integrated everywhere from our homes to our factories. However, their growing connectivity makes them susceptible to unauthorized access, which could pose serious threats to both personal and corporate data.
Measures that can be taken:
- Strong Encryption and Security Protocols: The security of IoT devices and the data communication between them should be ensured through encryption techniques and robust security protocols.
- Regular Software Updates and Security Patches: Keeping devices updated and promptly addressing security vulnerabilities are possible through continuous software updates and security patches.
- Comprehensive Network Security Policies and Device Management: Strengthening network security policies and effective device management reduce potential security risks in IoT devices and protect corporate data.
6- Critical Infrastructure Security
Critical infrastructures like power plants, water treatment facilities, and communication systems are increasingly under threat due to climate change and more frequent natural disasters. When these infrastructures are attacked, widespread outages and serious economic damages can occur. The security of these facilities is vital to prevent service interruptions and ensure the continuous functioning of society.
Measures that can be taken:
- Risk assessments and regular security audits.
- Quick response plans and continuous monitoring.
- Integration of physical security measures with cybersecurity measures.
Cybersecurity Threats: What Are We Facing?
With the acceleration of digital transformation, the variety and impact of cyber threats have increased. As the internet becomes central to our lives and artificial intelligence (AI) is used more frequently, deliberate actions intended to cause harm, steal data, or disrupt systems are also on the rise. Let's look at the most common types of cyber threats we face and how we can deal with them:
1- Phishing
Phishing is a common danger. It often occurs through emails that appear to be from a trusted source. Clicking on malicious links in these emails can lead to the installation of malware on computers or the theft of personal information.A precaution is to be careful with emails from unknown people that look suspicious.
2- Social Engineering
Social engineering involves tricking individuals into breaking security protocols or convincing them to divulge confidential information. This method is usually carried out under the guise of a trusted person or organization. Although similar to phishing, social engineering involves manipulating individuals more directly and in various ways. The best defense is to question the authenticity of incoming requests and always be cautious about sharing information.
3- Malware
Malware, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans, comes in various forms. These programs often infiltrate systems without the user's knowledge and can cause damage, steal data, or create openings for further attacks. The best way to combat malware is to use reliable antivirus programs and regularly update your systems.
4- Spyware
Spyware typically collects personal and financial information by monitoring users' behavior without their knowledge. This type of software can often come with other malware and seriously harm users' privacy. Protecting against spyware involves keeping security software updated and avoiding suspicious applications.
Dealing with these threats is possible with knowledge and the right tools. Taking necessary precautions and staying aware in the digital world is crucial for safety.
Tips & Tricks
Here are some simple steps that can make a big difference in reducing cybersecurity risks. Why not make these tips a part of your life to protect your digital footprint and use technology safely?
- Keep Personal Information Private: Do not share your personal information (such as birth date, mother's maiden name, passport number, etc.) with anyone.
- Beware of Scammers: Be cautious of social engineering techniques like phishing via email or smishing via SMS.
- Software Updates: Regularly update your software and enable automatic updates if possible.
- Create Strong Passwords: Use passwords that are at least 14 characters long, complex yet memorable.
- Two-Step Verification: Use two-factor or multi-factor authentication systems whenever possible.
- Leave No Trace on Shared or Public Devices: Always log out of your accounts after use and clear the browser history.
- Be Cautious with Free Wi-Fi: Avoid sharing sensitive information over open Wi-Fi networks.
- Manage Privacy Settings: Regularly check and manage the privacy settings on your devices and apps, and disable unnecessary permissions.
- Check App Permissions: Before downloading a new app, pay attention to the permissions it requests.
Real Life Examples
According to a 2023 Statista survey on the rate of cyber attacks in companies across the US and Europe, Germany emerged as the country most exposed to cyber attacks, with French companies following at 53% in reported cyber attack share.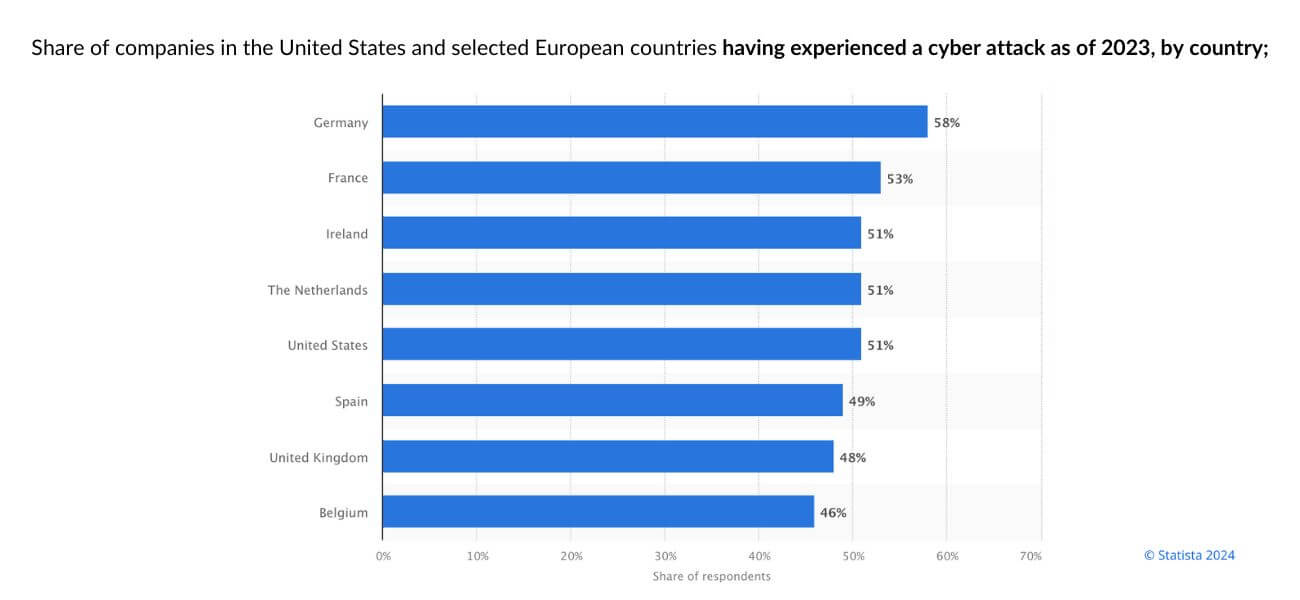
These data clearly show that cyber attacks are a global threat and are on an increasing trend.
The acceleration of digital transformation diversifies the areas and methods targeted by cybercriminals, making it essential to continually update cybersecurity strategies. By examining examples of recent cyber attacks, we can better understand the damage caused by threats and the necessary precautions to take:
MOVEit Zero-Day Exploit by Cl0p Gang (2023)
- What happened: In May 2023, the Cl0p ransomware gang exploited a zero-day vulnerability in MOVEit Transfer, a widely used secure file transfer software developed by Progress Software. The attackers gained access to MOVEit servers by bypassing authentication and stole customer data.
- Why it happened: Attackers exploited a previously unknown security vulnerability (zero-day) in MOVEit Transfer software.
- Effects and significance: This breach affected over 1,000 organizations worldwide and exposed the data of 60 million individuals. The Cl0p gang targeted a wide range of organizations including numerous government agencies, healthcare providers, and businesses like British Airways, Boots, and BBC. The breach is considered one of the biggest and most damaging cyber attacks in history, not only because of the number of people affected but also because of the financial losses and long-term impact.
Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack (2021)
- What happened: In May 2021, Colonial Pipeline, which transports gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel over 5,500 miles from Texas to New York, was targeted by the DarkSide ransomware group.
- Why it happened: Attackers accessed an old VPN system that did not include multi-factor authentication and placed ransomware that encrypted data across the network.
- Effects and significance: The attack forced Colonial Pipeline to halt operations, leading to significant fuel shortages and panic along the US East Coast. The company paid approximately $4.4 million in ransom to regain access to their systems. This attack highlighted how vulnerable critical infrastructure is to cyber threats and the widespread consequences such security breaches can have on national supply chains.
Heartland Payment Systems Cyber Attack (2008)
- What happened: In 2008, Heartland Payment Systems, one of the world’s largest credit card processors, handling about 100 million transactions a month for Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and Discover, was targeted by an SQL injection attack. This attack allowed attackers to manipulate the code of a web script and gain access to a web login page.Albert Gonzalez and two Russian hackers placed sniffer programs in the Heartland system to capture credit card information in real time and transmit it to themselves.
- Why it happened: Attackers exploited weak security protocols in the web application and a coding flaw vulnerable to SQL injection attacks. During this process, Albert Gonzalez managed to steal over 180 million credit and bank card accounts.
- Effects and significance: This attack is recorded as one of the largest credit card hacks in history. Approximately 130 million customer accounts were accessed. The attackers gathered enough data to produce physical credit cards. The attack went unnoticed for six months. Gonzalez was already under police surveillance for two other hacking incidents (Dave & Buster’s and TJX) when the sniffer programs were discovered, and the Heartland investigation began. In 2010, Gonzalez was convicted and received an unprecedented 20-year prison sentence. This event highlighted the deficiencies in authorities' efforts to prevent cybercrime and the need to protect critical infrastructures.
Top Trends in Cybersecurity for 2024
Prestigious organizations like McKinsey and Gartner released detailed trend reports on cybersecurity. These trends aim not only to create safer digital environments but also to strengthen proactive defense strategies against cyber threats.

Let's explore the cybersecurity trends that are expected to emerge in the next three to five years:
1- Continuous Threat Management and Third-Party Risks
As companies' digital footprints expand, they face constant threats. Factors such as the rise in SaaS usage, remote work, and the expansion of digital supply chains contribute to this change. Additionally, the likelihood of third-party providers experiencing cyber incidents pushes companies to make more resilience-focused investments in their relationships with these parties.
2- Identity Management and Access Control
The importance of Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems is growing due to their role in preventing data breaches. These systems manage user authentication and authorization processes, restricting inappropriate access and thus strengthening cybersecurity posture.
3- Artificial Intelligence and the Human Factor
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly becoming a part of our lives. Like in many areas, AI plays a critical role in developing cybersecurity strategies and can proactively support cybersecurity functions.
AI not only accelerates threat detection and response processes but also supports Security Behavior and Culture Programs (SBCPs), helping to promote safe behaviors among employees. These programs increase employees' security awareness, helping to prevent potential breaches.
Featured resource:
What is AI-Augmented Software Development?
4- Privacy-Focused Data Management and Cloud Security
Increasing privacy laws and data protection regulations require companies to review their application architectures and data management practices. Cloud security plays a critical role in maintaining security and compliance standards, even when data must be stored in a fragmented and distributed manner.
5- Evolution of Cybersecurity Skills and Operational Models
Traditional cybersecurity models are transforming as technology integrates more deeply into business functions. During this process, the skill sets of cybersecurity teams also need to evolve to keep up with current developments. Therefore, training and reskilling become even more crucial for both existing and new staff.
These five main trends indicate that it will be necessary for companies to reassess their cybersecurity strategies and implement effective defense mechanisms. New cybersecurity capabilities like zero trust architecture and behavioral analytics will play a significant role in this process.
The Future of Cybersecurity: Adapting to Technological and Business Changes
Cybersecurity will continuously evolve, shaped directly by technological advancements and changes in the business world. It will remain dynamic and proactive, requiring ongoing adaptation. Identifying new threats and discovering new ways to combat them will be a continually developing process.
Cybersecurity has become a key to success in the modern digital world, and investments in this field will form the cornerstone of security at both individual and corporate levels. Training and skill acquisition will always guide this process. IT training can enlighten employees about recognizing new threats and taking countermeasures, thereby fostering a cybersecurity culture and generating new strategies.
In summary, cybersecurity is not just a technological issue but also a strategic management concern. Businesses and institutions must adopt a proactive approach to threats and spread a culture of cybersecurity throughout their organization. This will help minimize current cyber risks and increase resilience against potential future threats.





