Key Takeaways
-
COBIT focuses on aligning IT strategies with business goals, managing risks, and ensuring IT processes meet stakeholder needs.
-
NIST provides a flexible framework for managing cybersecurity risks, suitable for organizations of all sizes and sectors.
-
COBIT is more prescriptive and geared towards IT governance, while NIST emphasizes cybersecurity risk management.
-
Choosing between COBIT vs NIST depends on whether the organization prioritizes IT governance or cybersecurity risk management.
Feel like you're wandering through a maze when looking at IT frameworks? Yeah, pretty overwhelming. With all the cyber baddies floating about, picking the right one is more important than ever to protect your organization's digital treasures.
We're breaking down two biggies in the IT management and cybersecurity world today:COBIT and NIST. Consider this your friendly guide to figuring out which might be your IT hero.
Let’s kick off with COBIT. Think of it like the Swiss Army knife in your tech toolkit. It’s all about lining up your IT plans with your business goals, keeping things running smoothly, and managing risks. With COBIT, you’re not just adding cool tech to your business; you’re making sure it really benefits your bottom line.
Then there’s NIST. Imagine a lighthouse guiding ships through the night that’s NIST for cybersecurity. Whether you’re a huge corporation or a small startup, NIST helps manage cybersecurity risks with globally recognized best practices.
Both frameworks have their perks for keeping your IT on point, but they cater to different needs. Whether you want to boost your cybersecurity or streamline your IT operations to better support your business objectives, getting a handle on COBIT and NIST can make a huge difference.Let’s dive deeper into their worlds and see which framework might be the best fit for your journey toward tech excellence and security.
What does COBIT stand for?
COBIT stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. It's like a secret recipe developed by ISACA to help businesses align their IT strategies with their overall goals. The focus is on improving IT governance, managing risks effectively, and ensuring that IT processes meet the needs of stakeholders.
The main goal of COBIT is to close the gap between IT operations and business objectives, making sure that investments in IT deliver maximum value while minimizing risks. It acts as a comprehensive guide for robust IT governance and management, helping organizations to achieve strategic goals and maintain regulatory compliance.
Since its introduction in 1996, COBIT has evolved through several updates:
-
COBIT 1 (1996): focused on IT control objectives for auditing.
-
COBIT 2 (1998): expanded to include guidance on IT management.
-
COBIT 3 (Early 2000s): integrated IT governance techniques.
-
COBIT 4 and 4.1 (2005, 2007): enhanced governance details for ICT.
-
COBIT 5 (2012): structured around risk management and governance.
-
COBIT 2019: the latest iteration, is designed to be more agile and integrates with contemporary IT practices like DevOps and Agile.
Through its various versions, COBIT has helped organizations optimize IT performance, manage risks and effectively achieve business goals in a rapidly changing technological environment.
Featured Resource:
COBIT Certification at a Glance - COBIT Framework
What does NIST do?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology is a U.S. agency specialized in the creation of standards, guidelines, and best practice drought on matters concerning cybersecurity. Basically, the institution looks to advance and improve cybersecurity in different sectors. It does so by providing a framework under which organizations can effectively deal with any risks associated with cybersecurity.
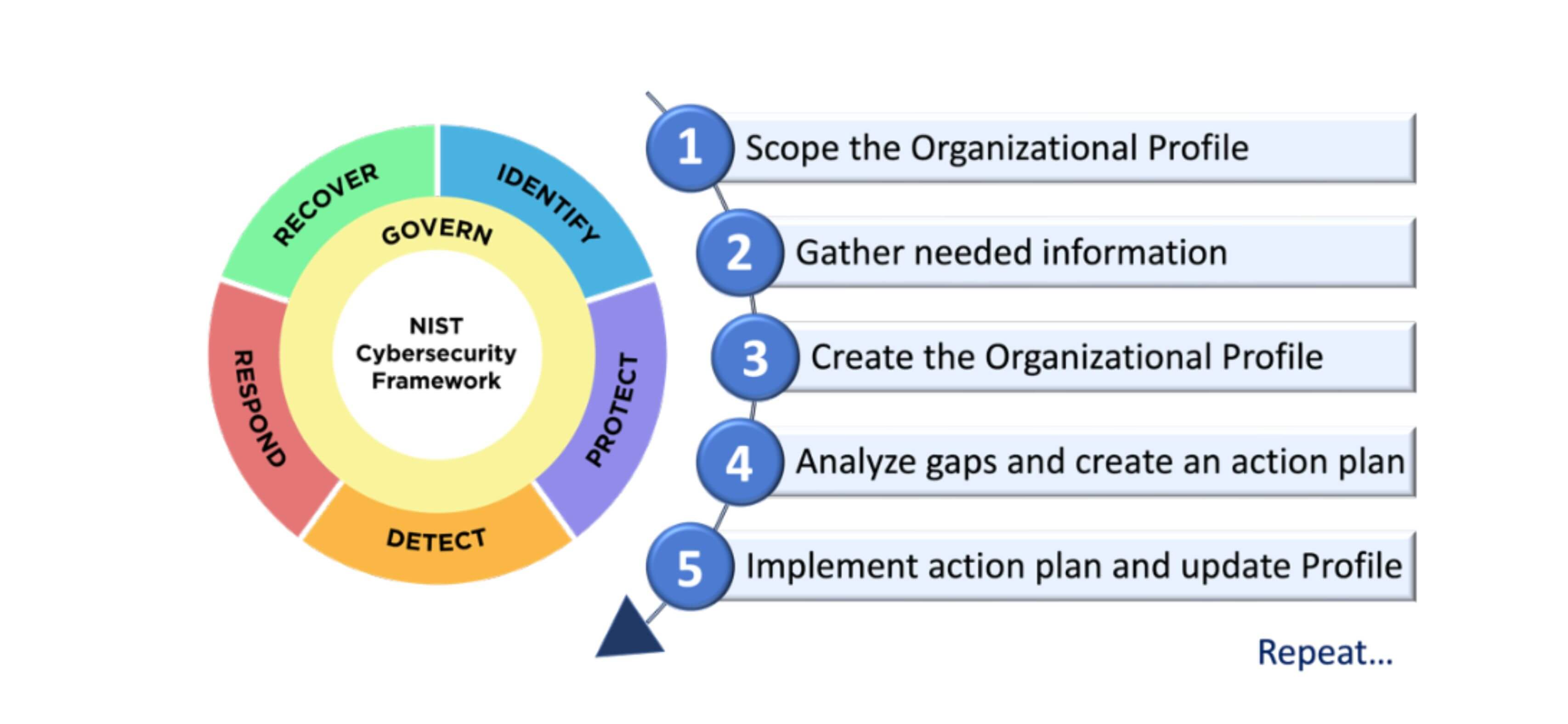
The five key core functions notably known to form the basis of NIST's Cybersecurity Framework are Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. These functions therefore aid an organization in designing a holistic cyber-security strategy, enhancing communications and collaboration between organizations locally and globally towards better cyber security.
NIST's Cybersecurity Framework was a product of the growing cyber threats that various organizations were facing at the time. The government, in collaborative efforts with private organizations and cybersecurity experts, developed this framework. This type of approach assures that it will accommodate the various needs and challenges of individual companies, increasing its applicability and effectiveness within the connected digital environment. The framework is designed to drive organizations toward taking an all-inclusive approach in the management and reduction of cybersecurity risks through assessment, protection, detection, response, and recovery processes.
Although NIST is based in the U.S., its standards have worldwide impact through the fact that they encourage international cooperation and compliance. The framework is further agile by the fact that it accommodates different organizations in terms of size and sector to implement and exercise necessary cyber security practices that are catered for; this common language—one through which standards are set—NIST enables collaboration between different organizations and various sectors, ensuring cohesion in cybersecurity. The efforts make NIST very instrumental in enabling organizations to prepare better against upcoming cyber threats and to manage their security risks more appropriately.
Featured Resource:
What Is NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
NIST vs COBIT: A Comparative Analysis
To determine which framework best fits an organization, it is essential to understand their structure, focus, and key features.
NIST Framework
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) version 2.0 is designed to help organizations manage cybersecurity risks effectively. Here's a simplified explanation of its main components:
-
CSF Core: This is the main part of the framework. It outlines a set of cybersecurity activities and outcomes that are understandable to everyone,whether they're experts or not. It's organized into Functions, Categories, and Subcategories that guide you through different cybersecurity tasks.
-
Organizational Profiles: These profiles help an organization describe its current and target cybersecurity states according to the CSF Core. It’s like setting a personalized cybersecurity goal based on the framework.
-
CSF Tiers: These tiers help an organization assess how advanced and thorough their cybersecurity practices are.They also provide a perspective on how seriously an organization takes its cybersecurity risks and what processes it has to manage those risks.
The CSF is versatile and can be used by any organization, regardless of its size or sector. It provides flexibility so each organization can adapt it to their unique risks, technologies, and missions. The framework is not mandatory; it’s voluntary and can be integrated with other resources to manage cybersecurity more effectively.
In addition to the main components, the CSF offers various online resources to help organizations adopt and use the framework. These include informative references, implementation examples, and quick-start guides, among others. These tools are designed to help organizations understand and implement the CSF effectively, set priorities for managing cybersecurity risks, and communicate about their cybersecurity posture both internally and externally.
COBIT Framework
COBIT stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. It is simply a collection of directives and recommended actions that assist in the more effective enablement of management and governance of enterprise IT.
Think of COBIT more as a toolkit that enables companies to assure the efficiency and business alignment of their IT processes. More importantly, it is the key to improved IT management, allowing appropriate technology for all stakeholders, including customers, employees, and investors.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
-
Framework: COBIT provides structured framework that will aid companies in the organization of their approach toward IT governance. It helps structure that information technology-based systems and processes support organizational strategies and objectives.
-
Stakeholder Alignment: This is ensuring that IT services are attuned to the requirements of whomsoever they depend on. Such alignment will, therefore, aid in delivering value to the business and satisfying stakeholder expectations.
-
Better Management: Following COBIT can help companies rationalize their IT operations to have lesser technical problems, reduced cost, and increased efficiency.
-
Risk Management: COBIT helps in identifying and managing the risks associated with IT, thus ensuring that information and the technology involved in an organization are safe.
-
Improvement: Applying the tenets of COBIT regularly puts an entity on the road to continuous improvement in IT service delivery and innovation.
In the instance of a bank, using COBIT can help resolve frequent IT-related issues, improve customer service, and enhance the overall performance and reputation of the organization. It is a very useful framework for any organization willing to have strong and efficient IT governance.
Featured Resource:
IT Certifications Compared: ITIL vs COBIT vs TOGAF
Key Differences
-
Emphasis: COBIT has much more emphasis on IT governance and alignment of IT with business but the NIST emphasis is anchored on the management of cybersecurity risk.
-
Structure: COBIT itself is structured on domains and processes that are orientated towards governance and management. Again, meeting NIST in this aspect, which is organized around key core functions with the aim of keeping risks at bay in cybersecurity.
-
Flexibility: NIST is considered to be more flexible and adaptable for a wide variety of industries, while COBIT is prescriptive in its application.
Key Features
COBIT:
- Now, there is a strong emphasis on the governance.
- Realignment of IT processes is done in accordance with business goals.
- Provides detailed guidelines and controls for IT management.
NIST:
- It manages cybersecurity risks.
- It provides a flexible framework adaptable to diverse industries.
- It gives a practically all-encompassing approach to cybersecurity threats.
How to Choose
Therefore, in choosing between COBIT and NIST, primary focus and requirements must be the determining factors for an organization. If a framework regarding IT governance and business objectives is sought, then COBIT would serve better. On the other hand,organizations envisioning creating a better cybersecurity posture may do so through NIST, which is focused on risk management coupled with flexibility.
In the end, though, the right choice between COBIT and NIST must be dictated by the unique requirements, industry, and goals of an organization. For some, the effective implementation of aspects of both types of frameworks gives an organization a whole IT assurance and security.